Before configuring Stage Triggers, it’s important to understand how your pipelines are structured—begin with An In-Depth Guide to Sales Goals and An In-Depth Guide to Marketing Goals, which explain how stages, goals, and opportunity movement function within each system. Once that foundation is in place, Stage Triggers are automation rules that operate directly within both Sales () and Marketing (
) pipeline stages, allowing workflows to respond automatically as opportunities and contacts move, engage, or change state. Their primary role is to ensure that key events inside either pipeline are recognized the moment they occur, helping teams enforce timing, prevent stalled deals, and maintain consistent process execution without manual oversight.
Then functions define what happens after a When function is activated. Once a triggering event occurs in a sales or marketing pipeline, the Then function determines the immediate action the system should take, allowing your workflow to respond automatically and consistently without manual intervention. These actions are designed to move work forward, update data, and initiate follow-up at the exact moment it’s needed. For a deeper understanding of how and when these actions are triggered, review the companion article on When functions, which explains the events that activate Stage Triggers and set these automated actions in motion.
In the sections that follow, we’ll explore each available Then function and explain how they can be used to automate communication, task management, pipeline movement, and system integrations that keep your processes efficient and aligned.
Then Functions — Table of Contents
- Update a contact field
- Create an opportunity
- Update an opportunity field
- Delete the opportunity
- Move to another stage
- Move to next stage
- Send an email
- Create a task
- Create a note
- Assign to user
- Assign to best performing user
- Send a template SMS
- Schedule a call
- Post webhook
- Move to pipeline
- Clone to pipeline
Update a contact field (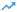 )
)
What it does
The Update a contact field Then function automatically modifies a specific field on a contact record when a trigger condition is met.
The Contact field selector determines which contact property will be updated (such as lifecycle stage, lead source, or a custom field).
The New Value field defines what that selected field should be changed to.
Examples of use
Lifecycle tracking: Automatically update a contact’s lifecycle stage when an opportunity reaches a key pipeline milestone.
Source attribution: Set or overwrite a lead source field when a contact engages at a specific stage.
Data normalization: Populate or standardize custom fields to keep contact records aligned with sales and marketing workflows.
Create an opportunity ( /
/ )
)
What it does
The Create an opportunity Then function automatically generates a new opportunity record when a trigger condition is met.
The Goal (sales only) field determines which sales goal the opportunity belongs to.
The optional Pipeline and Stage fields control where the opportunity is placed within that goal’s pipeline.
Additional optional fields—such as Title, Owner, Amount, and Currency—allow you to predefine key opportunity details, ensuring the deal is created with consistent structure and ownership from the start.
Examples of use
Inbound qualification: Automatically create a new opportunity when a contact reaches a qualified stage or submits a high-intent form.
Sales handoff: Generate an opportunity and assign an owner when a marketing-qualified contact enters a sales-ready stage.
Deal standardization: Ensure every new opportunity starts with a consistent title, value, currency, and pipeline placement for cleaner reporting and forecasting.
Update an Opportunity Field ( )
)
What it does
This Then function automatically modifies an existing opportunity when a Stage Trigger fires.
The Opportunity field determines exactly which attribute of the opportunity will be updated, such as the title, status, value, or a custom opportunity field.
The New Value field defines what that selected field should be changed to.
Examples of use
Standardize deal data: Update the opportunity title, status, or a custom field when a deal reaches a specific stage to enforce naming and classification rules.
Drive reporting accuracy: Automatically set fields like priority, deal type, or forecast category so pipeline reports stay reliable and up to date.
Trigger downstream automation: Populate or change opportunity fields that other workflows, alerts, or integrations depend on to function correctly.
Delete the Opportunity ( )
)
What it does
This Then function permanently removes an opportunity from the pipeline when a Stage Trigger fires. It is typically used to automatically clean up invalid, duplicate, or disqualified deals so your pipeline stays accurate and focused only on active, relevant opportunities.
Examples of use
Automatic cleanup: Delete opportunities when they enter a disqualification or closed-lost stage that should not remain in the pipeline.
Prevent clutter: Remove test, demo, or mistakenly created opportunities without requiring manual intervention.
Enforce data quality rules: Automatically eliminate opportunities that fail qualification criteria or violate predefined pipeline standards.
Move to Another Stage ( )
)
What it does
This Then function automatically moves an opportunity to a specific stage when a Stage Trigger fires.
The Target Pipeline field lets you choose which pipeline the opportunity should be moved within. a
The Target Stage field defines the exact stage the opportunity will be placed into, ensuring deals progress to the correct point in your workflow without manual action.
Examples of use
Automated progression: Move opportunities forward when key conditions are met, such as advancing a deal after a task is completed or a form is submitted.
Pipeline corrections: Automatically reposition opportunities that were moved incorrectly or need to be routed back to an earlier stage.
Cross-workflow routing: Send opportunities to specific stages based on engagement, qualification status, or internal review outcomes.
Move to next stage ( /
/ )
)
What it does
The Move to next stage Then function automatically advances an opportunity forward in its current pipeline when a trigger condition is met. Instead of selecting a specific destination, this action uses the pipeline’s existing stage order to determine where the opportunity should go next, ensuring consistent progression that follows your defined workflow without manual intervention.
Examples of use
Guided deal progression: Automatically move opportunities forward once required actions, such as task completion or engagement, have occurred.
Process enforcement: Ensure deals advance only after meeting internal criteria, reducing stalled opportunities and skipped steps.
Workflow automation: Create seamless, stage-by-stage movement that mirrors your sales process and keeps pipelines moving efficiently.
Send an email ( /
/ )
)
What it does
The Send an email Then function automatically delivers a predefined email template when a Stage Trigger fires. The Template selector controls which triggered email is sent, ensuring consistent and approved messaging, while Avoid Rules allow you to prevent delivery during restricted times such as weekends, holidays, or quiet hours. An optional Absolute cutoff can be set to stop the email from sending after a specific date and time, ensuring messages remain timely and relevant.
Examples of use
Immediate follow-up: Send a welcome or next-steps email as soon as an opportunity enters a new pipeline stage.
Compliance-aware messaging: Restrict emails from sending outside business hours or on account holidays.
Deadline-based communication: Automatically stop reminder or promotional emails after a defined cutoff date to avoid outdated outreach.
Create a task ( )
)
What it does
The Create a task Then function automatically generates a task when a Stage Trigger fires, ensuring follow-up actions are clearly assigned and time-bound.
The Task Title field defines what the task is (such as a call, email, or review).
The Due in Days sets how many days after the trigger the task should be due, helping teams stay organized and responsive as opportunities progress.
Examples of use
Sales follow-up: Automatically create a follow-up call task a few days after an opportunity enters a key stage.
Account management: Generate reminder tasks for reps to check in after demos, proposals, or negotiations.
Process consistency: Ensure every opportunity triggers required tasks so no critical steps are missed.
Create a note ( )
)
What it does
The Create a note Then function automatically adds a note to the contact or opportunity record when a Stage Trigger fires.
The Note text field allows you to define exactly what information should be recorded, creating a clear audit trail of important events, context, or internal updates as records move through the pipeline.
Examples of use
Activity logging: Automatically document when an opportunity enters a key stage or meets a specific condition.
Team context: Leave standardized internal notes to keep sales, marketing, and support teams aligned.
Process visibility: Capture important milestones or status changes without requiring manual note entry.
Assign to user ( )
)
What it does
The Assign to user Then function automatically assigns the contact or opportunity to a specific user when a Stage Trigger fires.
The Assign to field determines which user will become the owner, ensuring responsibility is clearly defined and records are routed to the correct team member at the right moment in the pipeline.
Examples of use
Lead routing: Automatically assign new opportunities to a designated sales rep when they enter an initial stage.
Ownership transfer: Reassign opportunities to a specialist or account manager as deals progress.
Workload control: Ensure records are consistently owned so follow-up and accountability are never missed.
Assign to best performing user ( )
)
What it does
The Assign to best performing user Then function automatically assigns an opportunity to the user with the strongest performance metrics when a Stage Trigger fires. Rather than selecting a fixed owner, this action dynamically evaluates user performance and routes the opportunity to the most effective rep, helping optimize conversions and ensure high-value opportunities receive immediate attention.
Examples of use
Performance-based routing: Automatically assign advancing opportunities to top-performing sales reps to improve close rates.
High-value prioritization: Route important or time-sensitive opportunities to experienced users without manual assignment.
Smart workload distribution: Balance opportunity ownership based on performance to reduce bottlenecks and keep pipelines moving efficiently.
Send a template SMS ( /
/ )
)
What it does
The Send a template SMS Then function automatically sends a predefined SMS message when a Stage Trigger fires.
The Template selector determines which triggered SMS template is used, ensuring messaging stays consistent and approved, while the Message Content field displays the exact text that will be delivered as defined in the template. This allows teams to deliver timely, automated SMS communication without any manual intervention.
Examples of use
Instant text follow-up: Automatically send a confirmation or next-steps SMS when an opportunity enters a new pipeline stage.
Time-sensitive engagement: Deliver SMS messages immediately when rapid contact is critical, such as after qualification or high-intent activity.
Consistent outreach: Ensure all SMS communications follow approved templates to maintain brand consistency and compliance.
Schedule a Call ( )
)
What it does
The Schedule a Call Then function automatically creates a scheduled call activity when a Stage Trigger fires. This action ensures that a call is placed directly onto the assigned user’s activity list at the exact moment it is needed, helping teams follow up promptly and maintain momentum as opportunities move through the pipeline. By automating call scheduling, this function removes the risk of missed or delayed outreach.
Examples of use
Immediate follow-up: Automatically schedule a call when an opportunity enters a qualification or negotiation stage.
Sales consistency: Ensure every deal receives a required call at key pipeline milestones without relying on manual reminders.
Timely engagement: Trigger call scheduling at moments of high intent to keep conversations moving forward efficiently.
Post webhook ( )
)
What it does
The Post webhook Then function sends a real-time HTTP request to an external system when a Stage Trigger fires. The URL field defines the destination endpoint that will receive the request.
The Payload (JSON or template) field controls the data sent, allowing you to pass structured information about the opportunity, contact, or event. This enables SalesNexus to communicate instantly with third-party tools, custom applications, or internal systems.
Examples of use
System integrations: Push pipeline updates to external CRMs, data warehouses, or analytics platforms in real time.
Custom automation: Trigger internal workflows or scripts when an opportunity reaches a specific stage.
Data synchronization: Send structured JSON data to keep external systems aligned with pipeline activity as it happens.
Move to pipeline ( /
/ )
)
What it does
The Move to pipeline Then function transfers an opportunity from its current pipeline into a different pipeline when a Stage Trigger fires. The Goal field specifies the destination goal (which must match the type of the current goal), while the Target Pipeline and Target Stage fields define exactly where the opportunity will land in the new pipeline. This allows opportunities to seamlessly transition between pipelines while preserving structure and reporting accuracy.
Examples of use
Pipeline handoff: Automatically move opportunities from a marketing pipeline into a sales pipeline once they meet qualification criteria.
Process segmentation: Shift deals into a specialized pipeline for renewals, upsells, or post-sale workflows.
Lifecycle progression: Ensure opportunities enter the correct pipeline and stage as they advance through distinct phases of your business process.
Clone to pipeline ( /
/ )
)
What it does
The Clone to pipeline Then function creates a duplicate of an existing opportunity and places the copy into a different pipeline when a Stage Trigger fires. The Goal field defines the destination goal (which must match the current goal type), while the Target Pipeline and Target Stage fields control where the cloned opportunity is created. An optional Title Suffix can be added to the opportunity name to clearly distinguish the cloned record from the original.
Examples of use
Parallel workflows: Create a duplicate opportunity in a separate pipeline for renewals, onboarding, or post-sale tracking.
Process branching: Maintain the original opportunity while sending a cloned version into a different workflow for specialized handling.
Clear record labeling: Automatically append a suffix such as “(copy)” to differentiate cloned opportunities in reporting and pipeline views.
You’re All Set
You now have a complete understanding of the Then functions that execute actions after a When function is met. By defining clear, intentional outcomes—such as updating records, sending messages, assigning ownership, or moving opportunities between stages and pipelines—you ensure that pipeline activity results in immediate, consistent, and measurable action without manual intervention.
With your actions configured, Stage Triggers become a powerful automation engine that enforces process, improves response times, and keeps both Sales and Marketing pipelines aligned. To revisit the event conditions that activate these actions, review Navigating Stage Triggers: When Functions and continue building automation workflows that respond precisely to real-world events and scale reliably as your team and pipeline grow.
To revisit how pipelines are structured and managed in the new SalesNexus experience, you can return to the detailed guides below:

Comments
0 comments
Please sign in to leave a comment.